Page 2
THE ECHO PERFORMANCE MODEL
1. ECHO performance framework
ECHO performance measurement framework is inspired in the well-accepted OECD health systems performance conceptualisation. Applied to a particular domain of interest, ECHO focuses specifically on utilization of effective care, equity in access, quality and safety, and efficiency.
A set of around 68 performance indicators, actually an adaptation and validation of those developed by different initiatives – AHRQ quality measures, OECD Healthcare Quality Indicators Program and Atlas VPM project – allows ECHO to operationalize those performance dimensions.
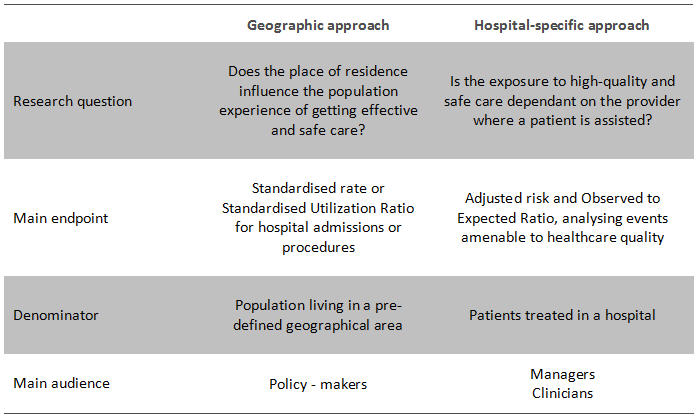
On the other hand, ECHO adopts two different methodological approaches; the first is based on a geographical perspective and accounts for the population’s exposure to health care; the second, hospital-specific, accounts for the patient’s experience in a particular provider.
While the former draws out evidence on equitable access to effective care, uneven exposure to ineffective care, and high (low) opportunity costs associated to the place where populations live, the latter elicits differences in quality of care, safety and technical efficiency that might be attributed to the providers where patients are treated.
ECHO methodological approaches:
Finally, the ECHO measurement framework seeks to provide two informative attributes for each performance indicator: the value and the variation. The value-attribute informs on whether performance reaches an acceptable level using a conventional benchmark. The variation-attribute signals whether the differences observed across territories or providers are systematic -as opposed to random.
2. How ECHO indicators inform performance
ECHO indicators operate differently depending on whether the perspective is geographic or hospital-specific, and also depending on the nature of the type of care under study.
3. Benchmarking in ECHO
An essential element in the ECHO performance measurement framework is the construction of benchmarks.
Given the advantage of the availability of individual-patient data in a single database, and the allocation of each hospital admission into a geographic area (place of residence) or into a hospital of treatment, ECHO is able to construct robust in-country and cross-country benchmarks.
In the case of the geographic analyses, the benchmark is determined by estimating the expected number of cases in a geographic area, either using a population of reference (direct standardisation) or the age-sex specific rates in the standard population (indirect standardisation). When the interest is in the national benchmark the standard of reference is the national “population”, while the ECHO population is used when the interest is in the international comparison.
In the case of hospital-specific analyses, the expected number of cases is estimated using logit-type multilevel analyses. When the interest is in national benchmarking the models use all the patients and hospitals in a specific country; in turn, international benchmarks are estimated using the whole sample of patients and hospitals in ECHO.
ECHO Atlases usually report performance indicators with both national and international benchmarks. But, ECHO allows benchmarking between pairs of countries, as well. This allows country A be compared with the best country within the ECHO sample, providing a sort of aspirational reference for each indicator.
Please cite this publication as:
European Collaboration for Healthcare Optimization (ECHO) www.echo-health.eu . Zaragoza (Spain): Instituto Aragonés de Ciencias de la Salud - Instituto Investigación Sanitaria Aragón; c2011. García-Armesto S, Bernal-Delgado E on behalf of the ECHO consortium. Handbook on methodology: ECHO performance model; 2014 Apr 27 [ accessed date ]; Available from: http://www.echo-health.eu/handbook/ performance_model.html